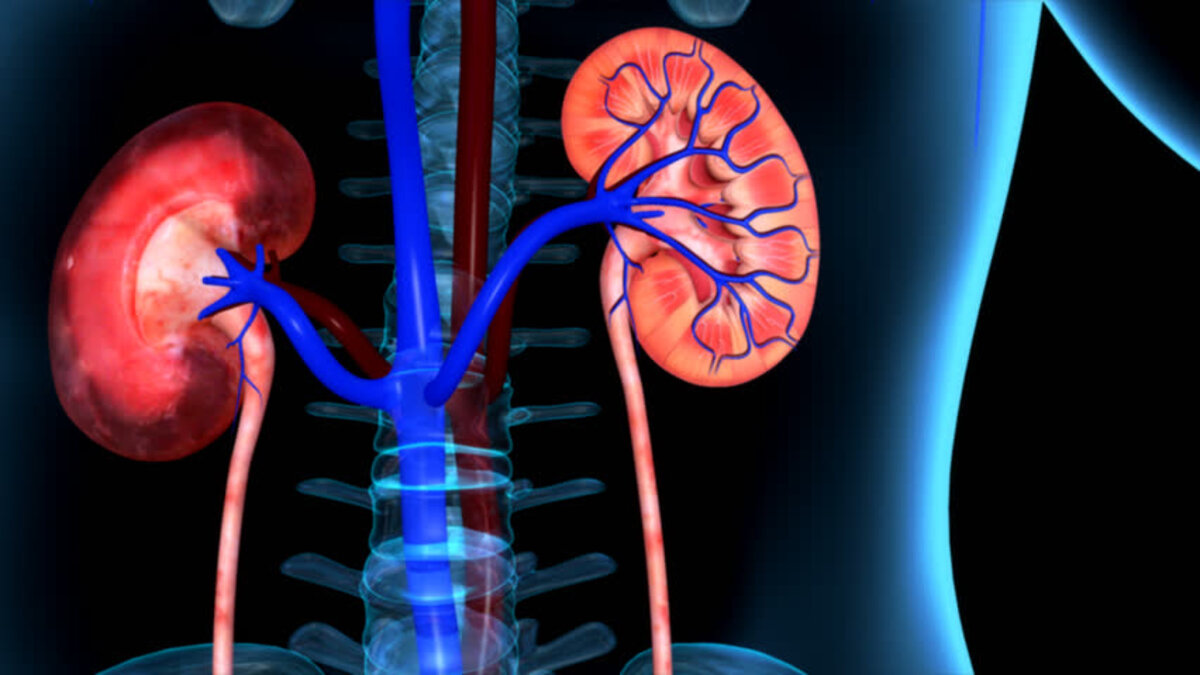
Kidneys are the organs responsible for excreting the wastes of the body particularly the end products of protein metabolism in the form of urine. Kidneys are composed of million functional units called nephrons. These nephrons function to filter the blood when it passes through the kidneys.
A kidney disease is an illness or disorder that affects the functions of the kidneys with regard to filtration, re-absorption and secretion. Kidney diseases can be hereditary, congenital or acquired.

Infection or inflammation of the nephrons leads to a condition called nephritis which can be easily managed through medication and diet but any structural or functional damage to the nephrons result in chronic kidney disease. This damage may leave kidneys unable to remove wastes. Usually the damage occurs slowly over years. If the damage is not repaired on time then it may lead to renal failure when dialysis or kidney transplant are the only options left. More so patient then has to be on a very critical diet support with only measured amounts of fluid and food allowed which is indeed painful.
Also Read: Ten Different Ways To Prevent Arthritis
A person should be careful to identify the symptoms and must undergo treatment as soon as possible. People who are obese or are suffering from hypertension, heart diseases or diabetes should be extra watchful as these conditions adversely affect the quality and flow of blood to the kidneys. These persons are strongly recommended to go for dietary management of kidney disease.
Dietary Management Of Kidney Disease
The dietary management of kidney disease should provide optimal nutritional support.
- Adequate protein should be taken unless oliguria (less urine formation) or anuria (no urine formation).
- Salt is restricted if there is edema, hypertension or oliguria.
- The fluid intake and the intake of electrolytes like potassium, calcium, and phosphorus should be adjusted according to the output including losses in vomiting or diarrhea.
- Foods low in sodium and potassium like apple, guava, papaya, pears and pineapple, should be chosen when there is oliguria.
- Foods low in protein and potassium and high in calories can be given freely like arrowroot, sago, unsalted butter, honey, etc.
Get a Renal Customized Diet Plan Made for Yourself Under Supervision of an Expert Nutritionist
It Helps
Diet Tips You Will Be Surprised To Know
- Sour lemon squeezed on food is an inexpensive and palatable form of taking vitamin C which promotes Iron absorption
- Germination and baking increases iron absorption.
- Prolonged warming of meals decreases their vitamin C content, and hence iron absorption.
- Tea and coffee form insoluble iron tannate that is not absorbed, hence it is not advisable to drink tea or coffee immediately after meals.
- Coconut milk, if used extensively in cooking inhibits iron absorption.
- When food is cooked in iron utensils, some iron is added from the utensils. When aluminium or stainless steel utensil are used, this source is lost.























[…] Also Read: Dietary Management of Kidney Disease […]